As a Company Manager, one of your main focus areas is to manage costs. Reducing operational and infrastructure costs are key to increase profitability and invest strategically. A recent study conducted by Waterstone Management Group, shows that small businesses spend close to $700 / year / employee for software, technical support and services. Each company is different, but I am sure your CPA group will calculate a similar figure for your last fiscal year.
So what can be done to reduce the cost of IT? As the title suggests, Cloud Computing can reduce and simplify your Information Technology infrastructure. The advantages of outsourcing your data and application management (when done right and with a reliable provider) are not only from an expenditure reduction perspective, but also by increasing stability, enabling mobility to your employees and increasing security. The next paragraphs will detail these four categories.
Expense Reduction
Let’s run an example that focuses on the reduction in IT expenditures. Forester, a global research and advisory firm published an article called “Should Your Email Live in the Cloud”. In this study and after reviewing financial data with several companies in the U.S., the average e-mail cost per year per employee was determined to be $302.16 when you include the following components:
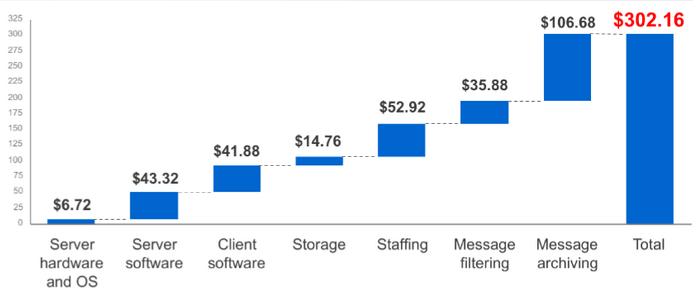
How does this compare to the Cloud? It wouldn’t be fair to just compare it against Google Apps Business + Google Vault ($100 / user / year total), since you still need to factor in Staffing in the cloud yearly price. However the cost in the graph at the top is only for e-mail, while Google Apps Business gives you other tools like chat, sites (a MS SharePoint equivalent), docs (unlimited storage for Google-type docs and 5GB of space for others) and mobile access.
An Example based on an 800 Employee Company:
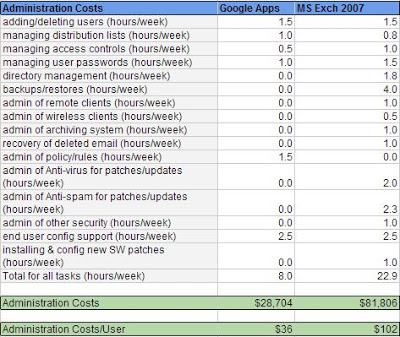
A different analysis was conducted by the Radicati Group called “Google Apps & Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 – Total Cost of Ownership Analysis”. This study was developed by Sarah Radicati, Ph.D., and utilized an example of a company of 800 users and an average salary of $69 / hour for Messaging Administrators to calculate the figures below.
Again each business is different and these figures represent an average based on the companies utilized for the sample. Your CIO and Finance group should have access to this information, but this model suggests you can reduce your Message Administrator workload by 2/3, which presents a situation where you can require a less skilled Administrator, outsource it to a Cloud Computing Reseller, or focus the Administrator on other activities that are more strategic for the company.
Down-time Impact
Now, let’s talk about stability or system down-time. The latest research from the Radicati Group found that on-premises email averaged 3.8 hours of downtime per month (2.5 are non-planned). Google Apps on the other hand has experienced an average of 7 minutes per user per month. These numbers estimate that Gmail is 32 times more reliable than the average email system, and 46 times more available than Microsoft Exchange®.
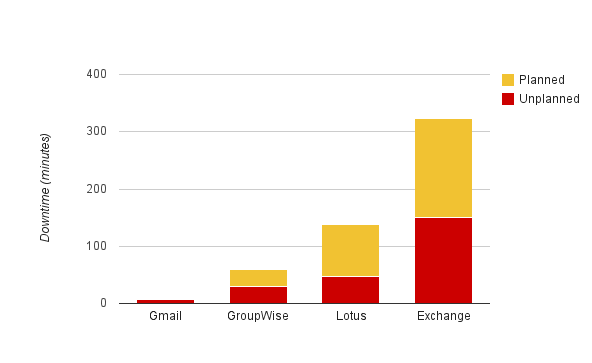
The Radicati Group, 2010. “Corporate IT Survey – Messaging & Collaboration, 2010-2011”
As a business manager, this data not only helps you compare which infrastructure gives your employees more headaches, but also put productivity and sales loss in terms of $$s. If we continue on the same example of a company with 800 employees, we can build a scenario to compare them.
This analysis will take a more strict approach and assume that Planned down-time does not affect regular users. From the graph above, we can compare 7 minutes of unplanned down-time for Gmail vs. 150 minutes for Exchange. The following assumptions are based on information collected from US statistics, but again, please consult with your IT, CPA and/or Financial group to plug your company numbers.
- Average Employee Salary: $25,560 / year
- Average Annual Hours / Employee: 2,080
- Total Employees: 800
- Users unproductive when e-mail is down: 50% estimated (400 employees)
- Company Annual Revenue: $2,000,000.00
- Revenue per Employee: $2,000,000 / 800 employees = $2,500
- Unplanned Monthly Email Downtime: 2.5 hours
With this information, you can estimate a productivity & revenue loss as a result of e-mail systems being down at $161,884 / year:
- Annual Productivity Downtime (hours): 400 employees x 2.5 hours x 12 months = 12,000 hours
- Annual Productivity Impact of Downtime: 12,000 hours x $25,560 / 2,080 hours = $147,461
- Annual Revenue Impact of Downtime: 12,000 hours x $2,500 / 2,080 hours = $14,423
- Compared to Google Apps Gmail with a 7 minute / month unplanned down-time, the results are $7,770 / year:
- Annual Productivity Downtime (hours): 400 employees x 0.12 hours x 12 months = 576 hours
- Annual Productivity Impact of Downtime: 576 hours x $25,560 / 2,080 hours = $7,078
- Annual Revenue Impact of Downtime: 576 hours x $2,500 / 2,080 hours = $692
- Net Savings: $154,114
Mobility
It is difficult to place a $$ figure when employees have better mobility tools, but it is clear that without a mobile workforce, companies run the risk of having higher costs. Empowering employees to access their e-mail, data and projects on the go can increase productivity by allowing information to flow faster, decisions made on the spot and quotes sent on-time. Also, when people get sick or need to stay home for urgent reasons, telecommuting becomes indispensable. With traditional infrastructures, there is a need to have a server on-site, install and maintain Virtual Private Networks, monitor firewalls and implement mobile redundancy systems. Most cloud applications and services eliminate the need of such systems and are included in the monthly or yearly fee.
Security
Now, with technology comes the risk of losing information. Nowadays losing information has a higher impact on revenue that losing equipment, and that loss can come from laptops being stolen, hard drives crashing, viruses or hackers. Consider the following statistics from Gartner (http://www.gartner.com/it/page.jsp?id=1862714) to give you a perspective of how real these are:
- 2 million + NBs are stolen every year; only 2% are recovered – FBI, 2008.
- 68% of Security Professionals say laptops pose the biggest security risk.
- 144 laptops were lost by the US FBI in the past 44 months
- Up to 13% of hard drives fail every year – Carnegie Mellon University, 2007
- 50% of computer users have lost or accidentally deleted files from their primary computer. – Chadwick Martin Bailey, 2010
- Companies take 25-56 days on average to apply O/S patches – during this time hackers work on reverse engineering and gaining access
How do these statistics help you compare costs between traditional tools and cloud computing? For one, Cloud Computing solutions eliminates the need to store data on the devices or use it as redundancy, enable mobile device remote wiping in the case of a stolen device, patches are released immediately, and viruses are not spread. For instance, Google keeps the data in a customized operating system to stop viruses on their tracks, and has data redundancy at multiple physical locations… when a system goes down, another one with the same data kicks in. Can your IT Manager say the same thing for your infrastructure? Consult your CIO and CFO and ask them how many computers have been reported lost, how many systems have crashed with unrecoverable data (and the recovered data… how many hours were spent), how much Staff you have on-site to control viruses, run backups and monitor your firewall. When you know the answer, you can plug the numbers to the conclusion below.
Putting It All Together
From the analysis above and excluding productivity gains from mobility or cost avoidance due to data loss, a company with 800 employees and revenue of $2,000,000.00 per year can find savings of $200K per year by transitioning to a cloud solution. Now, this analysis is for illustration purposes as each business is different and utilizes technology in a unique way; therefore a customized calculation would need to be created. Also, please know that this study excluded areas related to software (i.e. Microsoft Office which has a price of $300) and other hidden costs and productivity loss caused by traditional tools. Consider those when estimating your ROI.
We hope this information helps you get a more comprehensive view of Information Technology from a cost perspective.
